Academic Project - A multi-threaded text processor designed and implemented with an active pipe-and-filter-based architecture.
This commandline program reads in a text file, removes stop-words, non-alphabetic text, stems words into their root form using the Apache Lucene Word-Stemming library, and computes the frequency of each word term; printing the 10 most common in order of their frequencies.
Implementing the program with a modular pipe-and-filter architecture enabled easy extensibility of the codebase to include entirely new filters outside of the default three.
Two versions of the program were implemented, the first uses a standard active (multi-threaded) pipe-and-filter architecture, however, the second uses multiple instances of some filters in order to increase throughput but also address performance-bottlenecks at some of the pipes.
Both versions of the program were evaluated with various dataset sizes (of which some are included in the codebase), their executions were instrumented, and their performance characteristics stored in an internal data structure for later processing. Given the modular nature of the program, it could very well be extended to feed into a front-end UI or an analytics back-end if needed.
The user enters in from the command line an input file to process, the stop-words file to use, and one or more numbers which represent the filter operations to be performed on the file, in order. During operation, each filter's response-time is measured for later evaluation.
There are 3 available filters, represented by the numbers 1-3:
- RemoveStopWords Text Filter
- RemoveNonAlphabeticText Filter
- StemWordsToRoot Text Filter
Irrespective of the filter order, the program will always Compute the word-term frequencies.
The Apache Lucence Library (lucene-core-3.0.3.jar), is employed to perform word-root-stemming and stop-word removals operations.
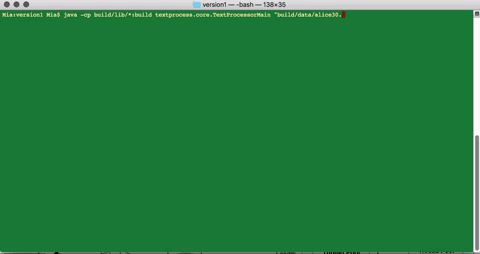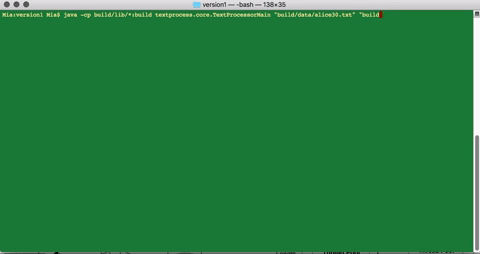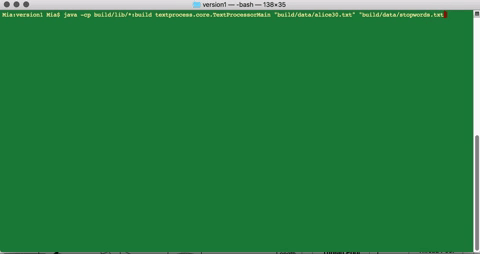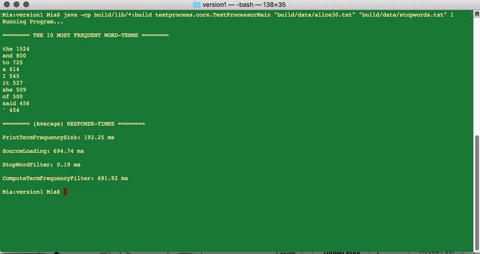
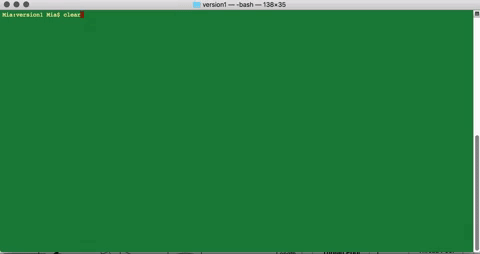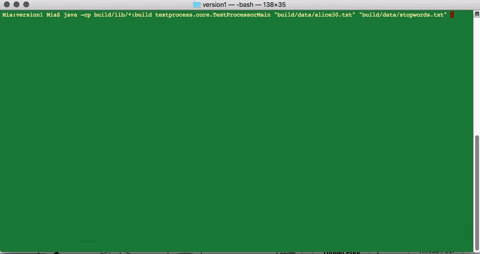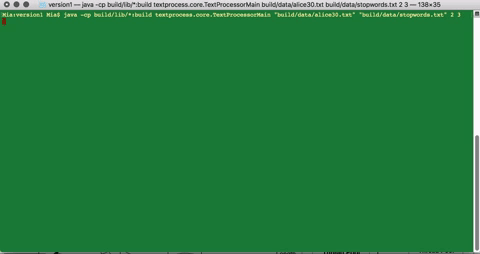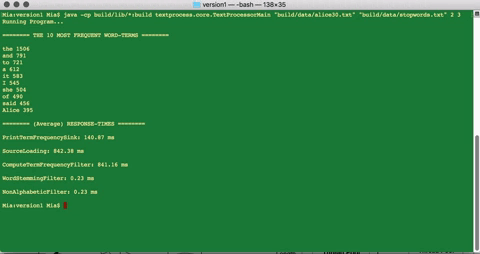
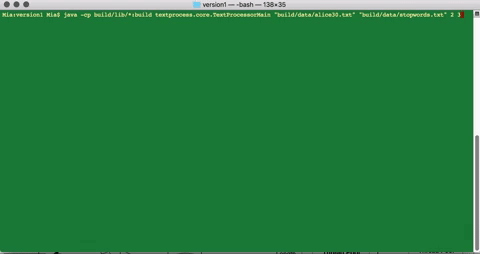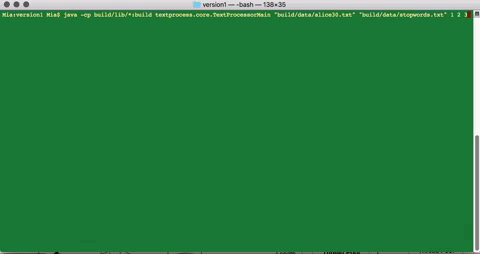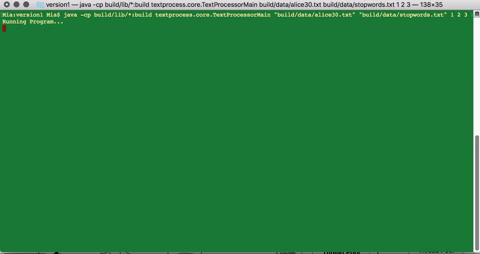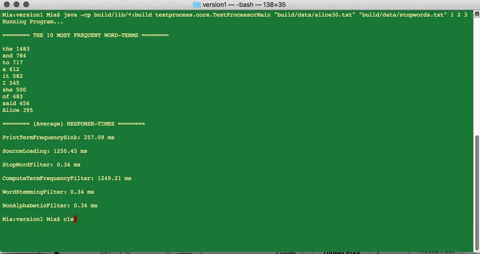
The final result of the filter operations is fed into a Data sink component which computes the frequency of each word-term in the processed-document and prints out, to the console, the 10 most common word-terms, along with the average response-times of each component.
The build folders of version 1 and 2, contain all the executable files needed for running the programs. Download the folder to your desktop first.
Open a terminal (or commandline shell) and navigate to the version's directory. i.e. '/version1/' or '/version2/' The format for running the program is:
>> java -cp <jar library_filepath>: textprocess.core.TextProcessorMain <input_filepath> <stopWord_filepath> filter_number(s)
For example, while in the 'version' directory:
This command will run the program on input file ‘alice30.txt’ with only text-filter 1
>> java -cp build/lib/*:build textprocess.core.TextProcessorMain “build/data/alice30.txt” “build/data/stopwords.txt” 1
This command will run the program on input file ‘usdeclar.txt’ with text-filters 1 and 2, in that order.
>> java -cp build/lib/*:build textprocess.core.TextProcessorMain “build/data/usdeclar.txt” “build/data/stopwords.txt” 1 2
This command will run the program on input file ‘usdeclar.txt’ with text-filters 2 and 3, in that order.
>> java -cp build/lib/*:build textprocess.core.TextProcessorMain “build/data/usdeclar.txt” “build/data/stopwords.txt” 2 3
This command will run on input file ‘kjbible.txt’ with all text-filters (1, 2, and 3) in that order.
>> java -cp build/lib/*:build TextProcessorMain “build/data/kjbible.txt” “build/data/stopwords.txt” 1 2 3